📝 Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized how we store, access, and manage data. It enables individuals and organizations to operate more efficiently and scale effortlessly. This guide walks you through the essentials of cloud computing.
☁️ What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of a wide array of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet, commonly known as “the cloud.” In the past, we used to procure all the servers, storage, and other infrastructure ourselves, which involved significant upfront costs and ongoing maintenance. This process required considerable time to procure the necessary hardware and accurately determine server specifications to avoid underutilization or over-specification.
However, with cloud computing, we can access and utilize these resources on-demand from a cloud service provider. This model allows us to purchase everything we need from a single company, which manages and maintains the infrastructure, ensuring scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency. This approach not only simplifies IT management but also enables businesses to focus on their core operations without worrying about the underlying technical complexities.
🔑 Key Characteristics
- On-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity
- Measured service
🕰️ History of Cloud Computing
- 1960s: Time-sharing on mainframe computers emerges
- 1999: Salesforce launches the first SaaS platform
- 2006: Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduces modern cloud infrastructure
- 2010s: Rapid adoption of Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and others
🧱 Core Components of Cloud Computing
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Compute | Virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing |
| Storage | Object, block, and file storage solutions |
| Networking | Load balancers, DNS, VPN, and firewall services |
| Databases | Managed SQL and NoSQL databases |
| Security | IAM, encryption, compliance tools |
| Software | SaaS platforms like Office 365 or Google Workspace |
🌐 Types of Cloud Computing
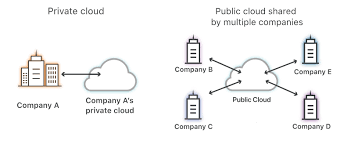
- Public Cloud: Operated by third-party providers. Cost-effective, less customizable.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated to one organization. More secure, more expensive.
- Hybrid Cloud: Mix of public and private. Flexible but complex to manage.
- Community Cloud: Shared by multiple organizations with common goals.
✅ Pros and ❌ Cons
Advantages
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Scalability: Add/remove resources easily
- Remote Access: Work from anywhere
- Resilience: Built-in disaster recovery
- Automatic Updates: Managed infrastructure
Disadvantages
- Security Concerns: Sensitive data in third-party hands
- Downtime Risks: Internet dependency
- Vendor Lock-In: Hard to switch providers
- Hidden Costs: Unexpected fees for bandwidth/storage
📊 Cloud Market Share (Q1 2024)
| Provider | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 31% |
| Microsoft Azure | 25% |
| Google Cloud Platform | 11% |
| Alibaba Cloud | 4% |
| IBM Cloud & Others | 29% |
Source: Synergy Research Group – Q1 2024
🔍 Popular Cloud Infrastructure Providers

- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Pros: Extensive services, strong global reach
- Cons: Complex pricing, steep learning curve

- Microsoft Azure
- Pros: Ideal for enterprise, Microsoft-friendly
- Cons: Interface can be overwhelming for newcomers

- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Pros: Excellent for AI/ML, Big Data
- Cons: Smaller ecosystem than AWS/Azure

- IBM Cloud
- Pros: Focus on security and hybrid cloud
- Cons: Fewer tools for developers

- DigitalOcean
- Pros: Simple, developer-friendly, affordable
- Cons: Limited for large-scale enterprise workloads
🧰 Popular Cloud SaaS Platforms
Cloud computing isn’t just about infrastructure—it powers tools we use every day.

- Microsoft 365
- Includes: Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, OneDrive, Teams
- Benefits:
- Real-time collaboration
- Integration with Windows
- Enterprise-grade security
- Drawbacks: Higher cost, heavier apps for casual users

- Google Workspace
- Includes: Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Drive, Meet
- Benefits:
- Simple interface
- Excellent collaboration tools
- Browser-native, minimal installation
- Drawbacks: Limited offline editing, basic formatting
- Zoho Workplace
- Includes: Zoho Mail, Writer, Sheet, Cliq
- Benefits:
- Cost-effective
- Lightweight, fast
- CRM integration
- Drawbacks: Less popular, limited integrations
🌟 Latest Trends in Cloud Computing
- AI-Powered Cloud: AI is becoming integral to cloud operations, optimizing resource allocation, automated scaling, and threat detection. This trend is driving unparalleled efficiency and cost reductions.
- Edge-to-Cloud AI Integration: AI workloads are dynamically shifting between edge and cloud environments. The cloud handles complex AI model training, while the edge manages real-time inferencing, ensuring rapid responses.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Enterprises are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to enhance flexibility and avoid vendor lock-in. This approach improves data storage management, disaster recovery, and security.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is streamlining infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus on building and deploying software services without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
- Green Cloud Initiatives: Sustainability is a growing focus, with cloud providers implementing green initiatives to reduce carbon footprints and promote energy-efficient data centers.
- Enhanced Security Measures: With the rise in cyber threats, cloud providers are enhancing security measures, including advanced encryption, AI-driven threat detection, and compliance tools.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing is emerging as a transformative technology in the cloud, offering unprecedented computational power for complex problem-solving.
- Increased Cloud Spending: Global public cloud spending is projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2027, highlighting the growing reliance on cloud services.
- PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS Solutions: The use of Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solutions continues to rise, providing modern service improvements and value to users.
📝 Final Thoughts
Cloud computing is more than a trend—it’s the foundation of modern business and technology. Whether you’re a startup or enterprise, cloud solutions help scale, save costs, and innovate faster.
From cloud infrastructure like AWS or Azure to SaaS platforms like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, choosing the right cloud mix is key to success.
Leave a Reply