📝 Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized data management by providing on-demand access to computing resources via the internet. This model allows businesses to access storage, computing power, and databases without investing in expensive physical infrastructure. In this guide, we will explore what cloud computing is, its core components, types, and how it can benefit your business.
☁️ What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet. These services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. Instead of purchasing and managing physical hardware, users access computing resources via cloud service providers, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. The cloud model offers businesses flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
Cloud computing eliminates the need for organizations to buy and maintain expensive IT infrastructure. Instead, they can rent resources as needed, with prices based on usage. This approach provides flexibility to scale operations up or down, depending on demand.
🔑 Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand Self-service: Users can provision and manage resources without requiring human intervention.
- Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the network from any device with internet access.
- Resource Pooling: Providers pool resources to serve multiple customers, sharing computing resources dynamically.
- Rapid Elasticity: Resources can be quickly scaled up or down to meet demand.
- Measured Service: Cloud resources are metered and billed according to usage.
🕰️ A Brief History of Cloud Computing
- 1960s: The concept of time-sharing on mainframe computers was born.
- 1999: Salesforce.com introduced Software as a Service (SaaS).
- 2006: Amazon Web Services (AWS) pioneered the concept of modern cloud infrastructure.
- 2010s: Other major players like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud began competing in the cloud space.
🧱 Core Components of Cloud Computing
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Compute | Virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing. |
| Storage | Object, block, and file storage options. |
| Networking | Load balancers, DNS, VPN, and firewalls for data traffic management. |
| Databases | Managed databases such as SQL, NoSQL, and data warehouses. |
| Security | Services like IAM, encryption, and compliance tools for security management. |
| Software | Software as a Service (SaaS), such as Office 365 and Google Workspace. |
🌐 Types of Cloud Computing
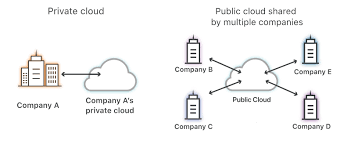
- Public Cloud: Services are delivered over the internet and shared among multiple users. Examples: AWS, Google Cloud.
- Private Cloud: Dedicated resources for a single organization, often used by large enterprises requiring higher security.
- Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds, allowing businesses to mix and match resources according to their needs.
- Community Cloud: Shared infrastructure for a group of organizations with similar goals or needs.
✅ Advantages and ❌ Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Advantages
- Cost Savings: Cloud eliminates the need for upfront hardware investments and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be scaled up or down based on demand.
- Accessibility: Cloud services are available from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Reliability: Cloud providers offer high availability and built-in disaster recovery.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud service providers manage updates, ensuring systems are always up-to-date.
Disadvantages
- Security Concerns: Data stored in the cloud can be vulnerable to breaches and cyberattacks.
- Downtime Risks: Cloud services depend on internet connectivity and may face downtime due to network issues.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving from one cloud provider to another can be difficult and costly.
- Hidden Costs: Unexpected charges for bandwidth and storage usage can arise.
📊 Cloud Market Share (Q1 2024)
| Provider | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 31% |
| Microsoft Azure | 25% |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | 11% |
| Alibaba Cloud | 4% |
| IBM Cloud & Others | 29% |
Source: Synergy Research Group – Q1 2024
🔍 Popular Cloud Infrastructure Providers

- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Pros: Extensive service offerings, global presence, and strong support.
- Cons: Complex pricing and a steep learning curve.

- Microsoft Azure
- Pros: Great for enterprises, integration with Microsoft products.
- Cons: Interface can be overwhelming for beginners.

- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Pros: Excellent for AI, machine learning, and big data.
- Cons: Smaller ecosystem compared to AWS and Azure.

- IBM Cloud
- Pros: Great for hybrid cloud and legacy systems.
- Cons: Smaller market share compared to others.
🚀 Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern business operations. It enables companies to access powerful computing resources without large upfront costs, scale effortlessly, and remain flexible. Understanding its core components and selecting the right provider is key to leveraging cloud technology for your business needs.
Explore more about cloud services, and feel free to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
Views: 19